The Best Tips To Help You Sleep Well
Are you tired of tossing and turning at night, struggling to fall asleep or stay asleep? If so, you're not alone. According to the National Sleep Foundation, more than 50 million Americans suffer from sleep disorders, and many more experience occasional sleep problems.
But don't despair - there are many things you can do to improve your sleep and wake up feeling refreshed. In this ultimate guide, we'll share 8 tips to help you sleep better at night, including:
Sticking to a consistent sleep schedule
Creating a relaxing bedtime routine
How improve melatonin production
Creating a sleep-conducive environment
Managing stress and anxiety
Using natural sleep aids
We'll also discuss the top 3 reasons why you may be having trouble sleeping, plus provide some beauty tips to help you wind down before bedtime.
So if you're ready to say goodbye to sleepless nights and hello to sweet dreams, read on and learn how to improve your sleep and wake up feeling energized and refreshed.
Contents:
Me and sleep
The different stages of Sleep
Sleep and the body repair processes
Sleep Hormones, Stress Hormones, and the Circadian Clock
The three top causes of insomnia
how Sleep affects your Height
your skin during sleep
6 Beauty tips you can take to bed
Weight loss and sleep
8 tips that can improve your sleep
This post contains links to the products that I use myself or can recommend. If you buy products through these links, the price will be the same for you, and I will receive a small commission, which helps to support this blog. This is my affiliate policy.
Me And Sleep
I went horseback riding in Iceland in September 2016 together with thirteen other women whom I’d never met before. We rode six hours a day in the fresh Icelandic nature, and at night we shared rooms in guesthouses two and two together. But despite plenty of fresh air and exercise during the days, most of us experienced trouble sleeping or slept very lightly during the nights. I have two theories about that: 1) Although the new company was both fun and inspiring, humans are basically gregarious animals keen to fit in, and depending on how sensitive you are it's mentally quite hard to adjust to a new group – most people are consciously and subconsciously more alert in those situations, thus it can be difficult to completely relax - even in your sleep. 2) The diet was very different from what I'm used to. I indulged in late night dinners, sugar desserts and gluten and dairy products, so my body was under an extra workload.
The trip was still amazing and fun, but when we landed in Copenhagen after the four days in the North Atlantic, several of us were really exhausted and needed solid restitution. My skin was saggy, because depending the quality of my sleep, my look can vary within a few days from looking ten years younger to resembling a nursing home resident. I’m very sleep sensitive and almost need as much sleep as a teenager I nevertheless sometimes really have a hard time falling asleep.
So, inspired by the sleep challenged ladies from Iceland and my own needs, I wrote this guide to a healthy and rejuvenating sleep.
The Different Stages Of Sleep
Sleep architecture follows a pattern of alternating REM (rapid eye movement) and NREM (non-rapid eye movement) sleep throughout a typical night in a cycle that repeats itself about every 90 minutes.
Each state and stage of sleep:
NREM (75% of night): As we begin to fall asleep, we enter NREM sleep, which is composed of stages 1-4
Stage 1: Between being awake and falling asleep
Light sleep
Stage 2: Onset of sleep
Becoming disengaged from surroundings
Breathing and heart rate are regular
Body temperature drops (so sleeping in a cool room is helpful)
Stages 3 and 4: Deepest and most restorative sleep
Blood pressure drops
Breathing becomes slower
Muscles are relaxed
Blood supply to muscles increases
Tissue growth and repair occurs
Energy is restored
Hormones are released, such as: Growth hormone, essential for growth and development, including muscle development
REM (25% of night): First occurs about 90 minutes after falling asleep and recurs about every 90 minutes, getting longer later in the night
Provides energy to brain and body
Supports daytime performance
Brain is active and dreams occur
Eyes dart back and forth
Body becomes immobile and relaxed, as muscles are turned off
Sleep And The Body Repair Processes
During sleep the body’s "cleaning night shift" goes to work, which:
Flush out waste toxins from the brain and the body.
Cleans the cells.
Repairs the heart and blood vessels.
Excretes accumulated fat.
Rebuilds the nervous system.
Processes the emotional impact and traumas we’ve been through during the day.
Moreover. When we sleep our brain triggers the release of hormones that encourages tissue growth. This can help us recover from injuries like cuts and abrasions or sore muscles.
Quality sleep also boosts the immune system as you produce more white blood cells during sleep, which attack viruses and bacteria. You can recover by yourself while sleepings – so to speak.
MORE: The 9 Best Brain Diet Tips That'll Boost your Mood, Memory & Focus
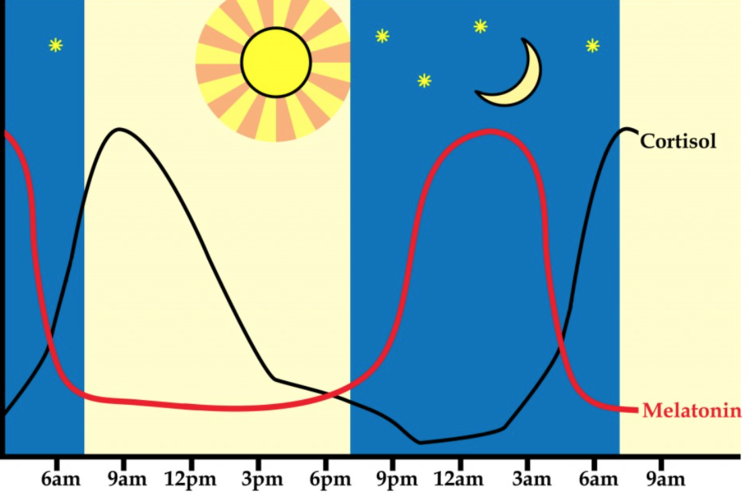
Sleep Hormones, Stress Hormones, And The Circadian Clock
" Hormones are like a symphony and circadian rhythms are the conductor." Uknown
Humans are diurnal animals, which means we’re naturally active during the daytime and our circadian rhythms reflect this. The circadian clock is set by a variety of external factors, but most importantly light during the day and dark at night. In order to have healthy circadian rhythms, your circadian clock needs to be set to the right time.
The hypothalamus, located in our brains, tells our bodies how to respond to the light and dark. When light hits the photopigment melanopsin in the retina, the hypothalamus tells our bodies to increase temperature, increase kortisol production, and decrease melatonin production. So when the melanopsin cells detect light (normally in the daytime), less melatonin is produced, making you feel more awake. When it is dark and melanopsin cells don’t detect light, more melatonin is produced, making you feel tired.
Cortisol
Short: Cortisol is the hormone that we release to wake us up and to respond to stress.
Cortisol is a naturally occurring hormone in our bodies and is secreted by the adrenal glands on a regular daily basis. Cortisol should be low at night while we sleep. It rapidly rises in the early morning, helping us have the energy to start our day. Cortisol is a wake-promoting hormone.
Our bodies release cortisol when confronted with stress. This is not necessarily a bad thing. Even when working out our bodies can release cortisol. In general, the release of cortisol is a perfectly normal response to help us biologically manage stress. Think of cortisol secretion in terms of our fight-or-flight response when in danger.
Cortisol is also a natural anti-inflammatory agent in our bodies.
On the bad side elevated levels of kortisol due to chronic stress means the body can no longer manage stress efficiently. Instead, the body ends up secreting a constant level of kortisol out of desperation, which over time, this starts to add a lot of wear and tear on our body, it causes inflammation, can increase abdominal fat, especially in women, and it suppresses another important hormone, DHEA, also called the "youth" hormone.
Cortisol causes blood sugar to elevate and this then leads to an acidic blood condition. Acidic blood leads to the modern life-style epidemics like diabetes, heart disease and cancer.
So we want to keep the cortisol level in the body balanced and deep sleep helps to negate the bad effects of cortisol.
Tip: As our bodies use cortisol to rescue us from low blood sugar, carbs is a tool you can use to help regulate your cortisol. Start your day with 25-35 grams of protein and finish it with 20-50 grams of high-quality carbs. Great options include paleo-friendly sources like sweet potatoes, turnips, squash, and beets. Having them later in the day helps not only cortisol, but a whole host of weight regulating hormones like leptin, ghrelin, and adiponectin.
Melatonin
Short: Melatonin is a hormone that causes drowsiness and a reduced core body temperature.
Melatonin is the body's natural sleep medication, and a hormone secreted in the brain at night by the pineal gland, so that we become drowsy and fall asleep. The function of the pineal gland is affected by light and darkness. Melatonin is produced and secreted primarily when it is dark, and as it’s important to maintain a nightly increase it’s essential to keep the bedroom totally dark. Even light from a street lamp can inhibit the production of melatonin.
The pineal gland is closely associated with the neuro-hormonal system, melatonin, zinc, selenium, the hormone-producing glands and the immune system. It’s all connected. The essential amino acid tryptophan you get from your diet is converted to the neurotransmitter serotonin and then in to melatonin.
The Fountain of Youth may be located in the pineal gland and in the melatonin. The nightly production of melatonin restores youthful levels of the hormone LH (Luteinizing hormone) in women during menopause. Within six monthsIt it can also recreate a youthful thyroid function in women aged 42-62 years.
Dr. Walter Pierpaoli who is the discoverer of melatonin's many qualities swapped the pineal glands in two mice, a grandfather and a nephew, and after a year there were no difference in the appearance and vitality of the two mice. Before the transplant the grandfather was clearly aged. Old pineal glands transplanted into young mice accelerates their aging. Melatonin also protects mice infected with a lethal virus.
New research shows that nighttime melatonin accounts for only 10 percent of our bodies' total melatonin? The other 90 percent of the melatonin we make happens in the daytime, and exposure to sunlight triggers that. The human body and our biology rhythms have evolved spending all day under the sun, so get outside during the day and let the sun hit your skin and eyes.
Dawn is the most important light for timing our circadian rhythm. The circadian rhythm is our biological clock, an internal timer set to a 24hrs rhythm. It's present in all life. It times all of our physiology and all of our behavior. The circadian Rhythm is set every day by the rising of the sun.
Melatonin And Cancer
Besides the fact that melatonin has an inhibitory effect on sepsis and other inflammatory conditions, melatonin is a powerful antioxidant, which partly counteracts the growth of blood vessels into tumours (angiogenesis) and prevents hormones, and also counteracts trace metastasis, partly stops the growth of cancer cells, and also make them commit suicide (apoptosis) and increase the activity of the immune system, particularly the number of so-called "killer cells" that attack and destroy cancer cells.
Read more about balancing hormones naturally here.
The 3 Top Reasons You Can't Sleep
1. Blue Light
Trouble sleeping? It might have something to do with what you’re looking at right now - the blue light that is.
The one thing that affects our circadian rhythm the most is the light/dark cycle of the earth, but like insulin and inflammation, blue light is essential to our health – in the correct amounts. When we’re exposed to levels of anything in excess (or too little) of what we would have experienced for the bulk of our evolutionary history, problems arise.
Blue light from a 10:00 AM sky or blue light from television or computer screen at midnight – it makes no difference to our circadian rhythms. It’s all the same to our bodies, because for millions of years blue light meant daylight, and it’s the blue light specifically that appears to monitor our sleep patterns the most. These days, though, we’re subject to a steady barrage of blue light. During the day, blue light (natural or unnatural) isn’t much of a problem because we’re supposed to be awake, but at night, when we’re “supposed” to be getting ready to sleep, we tend to sit in front of blue light-emanating appliances, and our sleep suffers for it.
Reddish light thought from fire (our formerly primary source of night time illumination) has little to no effect on melatonin production, so sleep isn’t disrupted when we rely on fire. Get tips to avoid blue light below.
2. Stress
Stress can be many things, but what typically is at stake is that your cortisol level is too high, either because you have a high tempo lifestyle, eat a diet that stimulates elevated cortisol, or because you stress yourself with your training - like hard endurance training, marathon training, extreme sports, extreme diets, very carbohydrates restrictive diet or a no fat diet. Hard training can provide such an increased level of the stress hormone cortisol in your body that you actually experience a state of elevated blood sugar even if you eat very healthy. Whether your cortisol levels are too high or unbalanced during the day or fluctuating - high and low - or you've almost no cortisol triggered during the day because you have pushed yourself for so long, that your body, your cells and, indeed, your brain is in a cortisol-marinade - it will affect your sleep, and you will have the same symptoms - you don’t feel fresh during the day, or just can’t get out of bed, or you have your energy in the evening when you're supposed to calm down.
3. Magnesium Deficiency
There can be many causes of insomnia, or a generally poor quality of sleep, but as mentioned above will specifically stress and blue light disrupt our cortisol / melatonin balance, but a magnesium deficiency can also be of cause. Due to modern farming methods and our diet today magnesium deficiency is fairly common. Magnesium is among other things important for muscle relaxation. I use magnesium daily in some form and use magnesium oil on my skin most often. There are some really high quality pre-made magnesium oils available now, but it is also very easy and cheap to make your own magnesium oil. I use the following forms of magnesium oil: I have previously written a detailed blog on this vital mineral and how to get enough of it.
How Sleep Affects Height
HGH (human growth hormone) is a peptide hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration. And in the early nighttime sleep cycle, we typically get a surge of that. This period of deep sleep, stages 3 and 4 sleep, contributes to the so-called "beauty sleep" as secretion of growth hormone helps repair and rebuild body tissues like muscle and bone. Many of the body’s tissues also show increased cell production and slower breakdown of proteins during this deep sleep. Since proteins are the building blocks needed for cell growth and for repair of damage from factors like stress and ultraviolet rays, deep sleep is truly "beauty sleep."
Sleep and Height
If you want to help increase the tallness of your children, make them sleep properly. The more deep sleep we get the more we will grow up until the age where our growth plates grow, which can be anywhere between the ages of 19-27. Essentially if your growth plates are open and you are getting growth hormone, then you will continue to get taller regardless of other factors. This is why it is so important for growing children and youths to get a lot of sleep in order to make sure they not only keep their bodies in good repair, but that they continue to grow into healthy adults.
You can encourage the body to produce more growth hormone by increasing how deeply you and your children sleep. Get the tips further down this post.
Your Skin During Sleep
Good and adequate sleep is important to the integrity of the skin as skin cells regenerate faster at night than during the day. Cell division happens throughout the day, but peaks around 2 am. This is literally renewal and rejuvenation during sleep. Although the peak in cell division happens even if you stay awake at night, the surge in growth hormone doesn't.
Increased growth hormone release is believed to be linked to the fasting state that the body enters during sleep. Contrary to what bodybuilders might want to believe, injections of growth hormone are more effective at stimulating collagen formation than preventing muscle atrophy. This suggests that naturally occurring growth hormone also plays a big part in maintaining collagen matrix, and hence the appearance of youthfulness. When rats are deprived of sleep, one of the early physical indications is lesion on the skin.
Sleep Hydrates The Skin
Sleep does lessen the severity of wrinkles in the neck and face, at least temporarily. Some smoothing is due to position - lying down diverts the force of gravity. But during sleep the whole body, including the face, also perspires more, this moisture on the skin smooth’s out wrinkles. Sleep is a natural moisturizer - perspiration during sleep is a natural skin treatment.
Radiance
The body cools in anticipation of bedtime (about half a degree) and to do so, the circulatory system increases blood flow to the skin. This is why the cheeks often flush at night. Radiance means that the colour of the skin moves closer to the colour of the blood
Beauty sleep is not a myth and sleep does lessen the severity of wrinkles in the face and neck, at least temporarily.
6 Beauty Tips You Can Take To Bed
Not only do the optimal seven to nine hours a night leave you looking luminous, but also many hair, face, and body products are most effective overnight because they penetrate better when you're at rest and work with the body’s higher state of repair mode. Since the body is in detox mode, it’s best to use as natural products as possible at night. Take advantage of sleep and wake up to these benefits:
1. Prevent “Sleeping Wrinkles”
Resting your face on the pillow in the same way every night for years creates the vertical wrinkles on the face and breast. Sleeping on the back prevents these wrinkles.
I use this “Save My Face” pillow to prevent the sleeping lines. It also eases tenderness and pains in neck, shoulders and back and improves breathing conditions.
2. Lip Care
For a really soft result exfoliate your lips using a wet washcloth, then swipe on a rich balm such as Soothing Lip Balm or another nourishing oil (olive, coconut or shea butter) – raw honey works well too and is calming. Another secret: Dab eye cream on your pout as these contain hydrating ingredients formulated for delicate skin.
3. No More Pimples
You can treat your blemishes while you sleep: apply a drop of tea tree oil on top of your pimple and see it diminish and disappear overnight. I've previously wrote more about acne treatment.
4. Smooth Feet
Massage Whipped Body Butter or a thick cream all over your feet, put on cosy cotton socks and go to sleep. In the morning your feet will be happy and smooth.
Get the whipped body butter recipe here or buy one from me.
5. Soft Hands
Apply Whipped Body Butter or a thick hand cream on your hands, put on light cotton gloves and leave this treatment on overnight. When you wake up your hands will feel very soft, moisturized and smooth.
Get the whipped body butter recipe here or buy one from me.
6. Sparkling Eyes
Store your eye cream in the fridge and apply it cool straight from there when you prepare to go to sleep. Not only it will help prolong the life of your product, but the cooling effect will also help to de-puff and soothe your eyes. My eye cream contains among other things avocado oil, cucumber extract, peptides, vitamins and ceramides, which lift, soothe and hydrate the delicate eye areas and reduce the appearance of wrinkles, fatty deposits, dark circles and puffiness, so that you will wake up looking fresh and rejuvenated.
Weight Loss And Sleep
Why is sleep might be the missing link for weight loss? I’ve got one word for you: Hormones.
Sleep deprivation causes hormone imbalance (Leptin, Ghrelin, kortisol, you name it). These out-of-balance hormones wreak havoc with appetite and metabolism. The result? When you are low on sleep, you’re more inclined consume extra calories, and you’re less able to burn off the calories and fat you consume.
Furthermore. When you sleep less, you burn fewer calories and burn less fat. Research indicates that a body deprived of sleep burns calories less effectively than a well-rested one. The body burns more calories in REM sleep than at any other stage of sleep. We experience longer periods of REM sleep as we move deeper into our sleep cycle over the course of a night. An abbreviated night of sleep cheats your body of the REM sleep that is prime calorie-burning time. Research also has shown that people who sleep less and still manage to lose weight will lose less actual fat.
8 Tips To Improve Your Sleep
1. Let the sun meet the eyes and the skin
Dawn is the most important light for timing our circadian rhythm. Our biological clock and internal timer is set to a 24hrs rhythm. It's present in all life. It times all of our physiology and all of our behavior. The circadian Rhythm is set every day by the rising of the sun.
All active processes are designed for daytime, and all restorative processes are kept to nighttime.
The human eye has an incredible ability to absorb and use sunlight.
When cells in our eyes detect that morning light, they send signals to different parts of your brain, which do several beneficial things, such as turning off the production of melatonin, the sleep hormone, in our pineal gland and helping increase cortisol, the waking hormone. We usually think of cortisol as a stress hormone, but our body requires a certain amount of cortisol to function, especially in the morning.
The main effect of morning light is to stimulate the main biological clock in our brain, which in turn synchronizes all the numerous clocks in our body to be in tune with the great natural rhythms of nature.
We live a very artificial life. Artificial life depends on artificial light. We give the body an incorrect time cue by seeking out artificial light. That's why you might feel far more alert at night and low during the day.
But if you start your day by going outside and getting some natural morning light in your eyes, it resets biological rhythms, primes your brain, and sets up your mood, focus, and energy. Plus it sets up a time release, so you sleep better at night.
2. Natures Sleep Remedies:
Magnesium: Spray on arms, legs, and stomach before bedtime. I use 10-20 sprays per day. It only takes five minutes to make your own or you can buy one here. Magnesium is essential for muscle relaxation, heart rhythm and health, blood vessels, airways ability to relax, skin, nerve function, mood, sleep, circulation of the important antioxidant glutathione, acid-base regulation, bone structure and organization, cleansing of waste products, immune functions and much more. I’ve written before about this important mineral.
Tart Cherry Juice:
* dry tissue, except for tart cherries and tart cherry juice concentrate
** average number – reported amounts were 90.7-450 ng/100g
*** average number – reported amounts were 13-29 ng/100g
Drink 1/4 cup of tart cherry juice (which actually doesn’t taste particularly tart) before bedtime. Tart cherry juice is nature's own sleep-inducer. As you can tell from the table the juice has a significantly high concentration of melatonin and can be used as natural sleep remedy and pain killer. A study published in the European Journal of Medicine i 2012 shows that tart cherry juice can improve the quality of your sleep, your sleep duration, and help reduce the need for daytime napping. The research team found that adults who drank two 1-ounce servings of tart cherry juice per day experienced a demonstrable increase in sleep efficiency as well as a 39-minute increase in average sleep duration.
Note that sweet cherries have 50 times less melatonin than tart ones; dried cherries appear to have none.
Honey and salt: Taking ½ tsp. raw (unpasteurized) honey with a little sprinkle salt helps sleep hormone production. Salt can help lower cortisol levels and balance blood sugar levels, which is what you want at night for restful sleep. Natural sugars can help by elevating insulin slightly, which helps lower cortisol
Nuts: Eat a handful of nuts an hour or more before bed. The tryptophan will help bring on sleep.
Other foods with a high content of tryptophan that you can easily incorporate into their daily diet are: poultry (especially turkey), fish (especially salmon), and beans and lentils.
Glycine: Consider also glycine, which is an amino acid - one of 20 used to make proteins in the human body. 3g of glycine an hour prior to sleep is able to increase sleep quality and improve self-reports of fatigue and well being the next day due to better sleep. You can get it in its purest form from MYPROTEIN. I get my glycine through my marine collagen powder and gelatine powder. It’s an American brand, and the cleanest I've been able to find. Most protein powders contain large amounts of glycine though, so if you don't have patience with the European customs barriers, then these Nuzest protein products are also very clean, with no artificial sweeteners, and has really good taste.
These things will keep you awake:
The caffeine intake after 2pm
Alcohol: While alcohol can cause drowsiness, the presence of alcohol in the body can keep it from entering the deeper and more regenerative sleep stages.
High carbohydrate snacks, especially grains and sugars will raise blood sugar and prevent you from falling asleep.
recipe of Goodnight Fruit Gummies
This recipe combines honey, salt, glycine, and cherry juice and is a perfect evening snack. You can give one to your child at night too. My own grown-up son loves them.
Ingredients:
2 cups tart cherry juice
½ cup gelatin powder
⅓ cup raw honey
Salt to sprinkle on top (optional)
1 tsp Vitamin C powder (optional)
Instructions:
In a small saucepan, slowly mix the gelatin powder into the juice.
Turn on low heat and stir as it begins to warm.
Stir for 2-3 minutes or until mixture is smooth and gelatin has dissolved.
Remove from heat and mix honey into the juice
Add Vitamin C if using.
Pour into silicon molds or a glass baking dish that has been greased with coconut oil.
Place in the refrigerator for 2 hours to harden and remove from molds.
Store in an air tight container in the fridge for up to 2 weeks (if they last that long,,,)
3. How To Avoid The Blue Light At Night
Dim all the lights at least an hour before bedtime and turn off unnecessary lights.
Keep electronics usage to a minimum or completely eliminate blue light (alarms, TVs, laptops, mobile phone, tablet etc.) after dark.
Another solution is to wear orange safety glasses at night. I use these ones every night. These are also good. Or these if you wear reading glasses.
Install F.lux (totally free) on your computer to cut down on blue light emissions.
Use candlelights instead of electric lamps
Go to sleep earlier.
Also, don’t forget to expose yourself to blue light during the day so that your cycle normalizes – it goes both ways.
4. Create A Good Sleep Environment
Calm, cool and dark is a good basic cocktail for the perfect sleeping environment.
Sounds: If your cortisol level is a bit high due to stress or you’re just generally sensitive to sounds, then you’ll consciously or subconsciously be more alert to sounds or potentials of noises, which will affect the quality of sleep.
I live in the centre of Copenhagen, so I very often sleep with these quite effective 3M earplugs designed for industry workers. I cut off the ends and strings. They are soft and comfortable, so you can easily wear them for long. They work by making a small negative pressure in the ear, and thus excludes almost all sound (you won't miss the alarm clock though).
Darkness: Keep your room as dark as possible and your sleeping quarters pitch black, so dark that you can’t even see your hand in front of you. Remove all sources of light from your bedroom or cover with heavy paper, cloth, masking tape etc.
You can use a sleeping mask or an eye pillow if you sleep in a hotel or the like or if the light still disturbs you or wake you in the morning. Lavender eye pillows can be extra relaxing. I use it this silky sleep mask that excludes all light.
Room temperature: Keep the bedroom at 18C / 65 F or below for best sleep. Bundle up or wear socks if you are cool natured, but keep the thermostat low. The body’s temperature naturally drops during the night, and studies show that a room temperature that mimics this is most conducive to quality sleep.
5. De-stress:
A stressed body has a challenged immune system. Here is an easy and effective way to calm the body morning, evening or whenever necessary. Doing this exercise daily diminishes stress substantially.
Lie every morning and every evening with legs up against a wall for 10 to 15 minutes – preferable with the open window - access to fresh air.
Start by taking 10 deep breaths in this way:
Count to 4 on the in-breath, count to 7 holding the breath and exhale on the count of 8
Finish with a 10-minute meditation
6. Chanting And Mantras
The brain loves to be active and helpful all the time, so an effective way to disconnect it, is to bore it. When you repeat the same word or phrase over and over again, the brain begins to get bored, and you tend to fall asleep. Be aware though that the "helpful" thoughts tend to sneak in anyway now and again, when that happens it’s important to return to the mantra continuously.
A mantra can be a word or phrase of your own choice you to repeat for yourself.
I use the following Hindu mantra that works every time for me. I say it 108 times, and use my mala chain to keep count.
Mantra: Om Gam Ganapataye Namaha
You can listen to it on Spotify: The long version or a short and beautiful version
Or listen to this wonderful soporific meditation music
7. Self Hypnosis
Deepak Chopra has recorded some pretty effective “bedtime stories”.
Try this guided walk on the beach.
Or this progressive muscle relaxation exercise.
8. Wake Up “Naturally”
Trade your noisy alarm clock out with this little sunlight device, which will wake you much more harmoniously. I use this one. It slowly brightens – just like a sunrise.
Goodnight and sleep tight
“Your body is made to be healthy and thriving. If your health is not where you want, please know it can improve. Never give up on yourself!” -Alan Christianson, NMD. Author of The Adrenal Reset Diet.
Dislaimer:
All information in this blog is strictly for informational purposes only and should not be taken as medical advice. The statements made in this blog have not been evaluated by The Danish Health Authority. The products linked to in this book and any information published in this blog are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. The information provided by this blog is not a substitute for a faceto-face consultation with your physician, and should not be construed as medical advice. The entire contents of this blog are based upon the opinions of Hanne Robinson. By reading and using this blog, you agree to only use this publication for personal informational use and not as a substitute for medical or other professional advice.