Collagen - The Secret To Vibrant Skin And A Supple Body
I have been eaten fish collagen daily for about a year now, and that is probably one of the best beauty / health products if you want profound change for the better. I've become stronger, I recover faster after training, I'm not stiff in my joints in the mornings anymore, I'm more supple, I sleep deeper, and my skin has become firmer and more hydrated.
I might begin to sound like one who aspires to a job as a demonstrator in the local supermarket right now, but the fact is (as we say in rehab) I find it hard to live without my white powder now.
I have just spend a month in Sinai, where I ran out and had to do without it for 14 days. And, to my surprise I quickly noticed the difference. My flexibility was the first thing that suffered, but my skin also soon went dry and I didn’t sleep so deep anymore. However. After just a few days of taking my white powder again, I immediately slept better and the old joints loosened up again!
This post contains links to the products that I use myself or can recommend. If you buy products through these links, the price will be the same for you, and I will receive a small commission, which helps to support this blog. You can read about my affiliate policy here.
So What Is Collagen?
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body, it is found in muscles, bones, skin, blood vessels, digestive system and tendons.
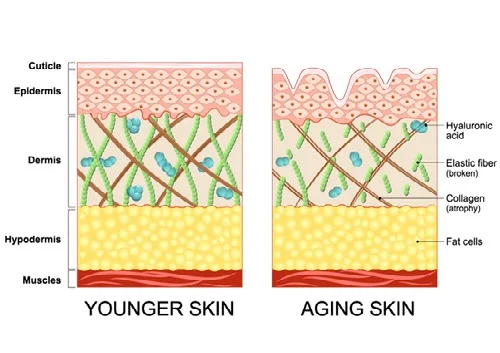
It is what helps give our skin strength and elasticity, along with replacing dead skin cells. In our joints and tendons, it is the “glue” that helps hold the body together.
Collagen is a hard, insoluble, and fibrous protein that makes up one-third of the protein in the human body. The collagens in the human body are strong and flexible.
Collagen is a long-chain amino acid and composed of the individual amino acids Glycine, Proline, Hydroxyproline and Arginine and in nature found exclusively in animal tissue, especially bones and connective tissue.
Collagen is secreted by various cells, but mainly by connective tissue cells.
In most collagens, the molecules are packed together to form long, thin fibrils (microscopic, thread-like structure of cells and tissues). These act as supporting structures and anchor cells to each other. They give among other things the skin strength and elasticity.
Endogenous collagen is natural collagen, synthesized by the body. Exogenous collagen is synthetic. It comes from an outside source, such as supplements.
Types Of Collagen
There are at least 16 different types of collagen, but 80 to 90 percent of them belong to types 1, 2, and 3. These different types have different structures and functions.
Type 1 collagen fibrils are stronger than steel and particularly capable of being stretched.
This is by far the most abundant, and almost considered to be the strongest, type of collagen found in the human body. It is made up of eosinophilic fibres that form parts of the body, including tendons, ligaments, organs and skin (dermis). Type 1 collagen also helps form bones and can be found within the digestive tract. It is very important for wound healing, giving skins its stretchy and elastic quality, and holding together tissue so it doesn’t tear.
Type 2 collagen primarily helps build cartilage, which is found in connective tissues. The health of our joints relies on cartilage made of type 2 collagen, which is why it is beneficial for preventing age-associated joint pain or various arthritis symptoms.
Type 3 collagen is made of reticular fibres and a major component of the extracellular matrix that makes up our organs and skin. It is usually found with type 1 and helps give skin its elasticity and firmness. It also forms blood vessels and tissue within the heart. For these reasons, deficiency in type 3 collagen has been linked to a higher risk for ruptured blood vessels and even early death.
Type I collagen and type 3 collagen are the major components of skin, hair, nails, muscles, tendons, ligaments, bones, gums, teeth, eyes and blood vessels. Together, types 1 and 3 collagen make up by far most of the collagen in the body.
Why Is Collagen Important?
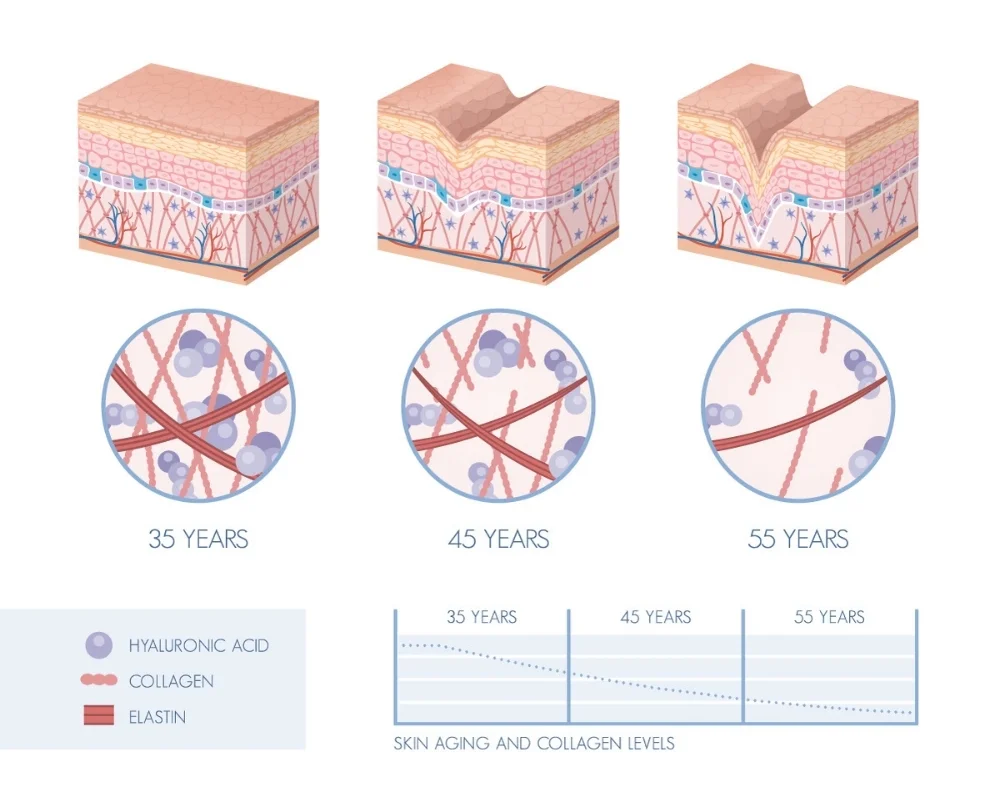
Our body’s collagen production naturally begins to slow down as we age. We can thank this degenerative process for signs of aging, such as wrinkles, sagging skin and joint pains due to weaker or decreased cartilage, but if you live a life where you indulge in sugar, smoking, alcohol and high amounts of sun exposure — it also contribute to depleting collagen levels. (1)
With age, the body produces less collagen. The structural integrity of the skin declines. Wrinkles form, and joint cartilage weakens.
Women experience a dramatic reduction in collagen synthesis after menopause.
By the age of 60 years, a considerable decline in collagen production is normal.
Factors That Work Against the Development Of Collagen
Aging
Alcohol
Dehydration
Drugs
Fluoridated water
Hormonal changes
Hydrogenated oils
Nutritional deficiencies
Overwork
Poor gut Health
Processed foods
Radiation
Stress
Sugar
Too much sun
Trauma
The good news is that these changes do not seem to be permanent or irreversible. In fact, a double-blind placebo study conducted in 2014 found that women who took collagen hydrolysate (the peptide form) regularly for 8 weeks saw a 20% reduction in wrinkles!
7 Beauty And Health Benefits Of Boosting Your Collagen
Note that many skin and hair products containing collagen claim to revitalize complexion and hair by increasing collagen levels within the body.
This is unlikely given collagen molecules are too large to be absorbed through the skin.
The real benefits come from within, not from a topical treatment.
There are several ways you can boost your body's collagen level. The two most effective are eating bone broth or eating a collagen dietary supplement - both can improve body, skin and psyche in these seven (and more) areas:
1. The Skin
Regardless of age collagen can improve acne and skin tone, help your skin look firmer, increase smoothness, and help your skin cells keep renewing and repairing normally.
Collagen also reduces cellulite and stretch marks. When skin loses its elasticity as a result of decreased collagen, cellulite becomes more visible. Improving your skin’s elasticity through collagen helps reduce that dimpling on your skin.
2. Sleep
Due to its content of glycine, collagen helps provide a deeper sleep and it releases the neurotransmitter serotonin - serotonin regulate feelings of happiness / content and sleep.
MORE: Top Tips to Help You Sleep Well, Lose Fat & Look Better
3. The Gut
Collagen improves gut health and digestion. The biggest digestive benefit of consuming more collagen is that it helps form connective tissue and therefore “seals and heals” the protective lining of the gastrointestinal tract keeping food particles and bacteria inside the gut where they belong, rather than allowing tiny openings to form that pass particles to the bloodstream where they trigger inflammation.
In addition to helping heal leaky gut, collagen also helps with the absorption of water within the intestines, keeping things moving more freely out of body.
Studies have found that in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, serum concentrations of collagen are decreased. Supplementing with collagen can help treat gastrointestinal symptoms and disorders, including leaky gut syndrome, IBS, acid reflux, and Crohn’s disease.
4. Muscles And Metabolism
Collagen builds muscle and repairs tissue for optimal workout recovery, supporting ligaments and tendons.
Retaining muscle mass is crucial as you age, since it helps support posture, bone health and burns more calories than fat.
Glycine has been found to help inhibit the deterioration of valuable protein tissue that forms muscle and boosts muscle recovery. In fact, it is known as an “anti-aging amino acid” because of how it helps maintain lean muscle mass into old age, stimulates the secretion of humangrowthhormone, prevents loss of cartilage in joints, and even improves daytime energy, physical performance and mental capabilities (all important for athletes). (2,3)
Glycine also helps provide cells with energy, feed muscle tissues and boosting endurance and strength. It also has benefits when it comes to hormone production and regulation, helping the body naturally synthesize steroid hormones that regulate the ratio of fat to muscle mass and control energy expenditure.
5. Joints
With its gel-like, smooth structure that covers and holds our bones together, collagen allows us to glide and move without pain. Think of ingesting more collagen like greasing a creaky door hinge: It helps your joints move more easily, reduces pain often associated with aging. It is no surprise that studies have found that collagen is an effective treatment for treating osteoarthritis and other joint pain and disorders. (4,5)
Collagen can treat osteoarthritis that can wear away cartilage, and bring pain relief and strengthen bones. Osteoarthritis, which is a disease that wear away cartilage in the joint gradually.
Collagen gives the cartilage tissue stretch strength and makes it stick together. Under normal conditions, the body will produce the complex molecules that make up cartilage tissue, but for many people the ability to maintain the cartilage tissue decline as they age. New research shows that a supplement of collagen can lead to better maintenance of the joints - thus avoiding discomforts like pain and stiffness in joints.
6. Supports The Detoxing Processes
Glycine in collagen and bone broth helps minimize damage your liver experiences when it absorbs foreign substances, toxins or alcohol pass through it.
Studies have even found that glycine can be used to help reduce alcohol-induced liver damage and other forms of acute or chronic liver injury.
7. A Healthy Heart
Collagen can be an important compound in maintaining a young and healthy heart.
The amino acid proline helps your artery walls release fat build-up in the bloodstream, shrinking the fat in the arteries and minimizing fat accumulation. Proline is needed for tissue repair and arteries, plus it helps control blood pressure.
In addition, arginine helps with nitric oxide production, which allows for better vasodilation — meaning the widening of arteries and relaxation of muscle cells and blood vessels that allows for better circulation.
3 Ways To Boost Your Collagen
As collagen is only stored in animal bones, you’ll likely have a more difficult time keeping up your collagen intake if you’re vegan or vegetarian, but there are ways you can boost it anyway – see point 3 below.
Note that when consuming collagen, you can benefit from also consuming vitamin C to ensure your body can convert the collagen into a useable protein.
1. Bone Broth
Collagen stored in animal bones is one of the reasons why bone broth is now considered a superfood.
As it slowly cooks down, collagen leaches out of the bones bringing healing benefits when consumed: soothing achy bones and muscles, fighting infection and inflammation and naturally increasing your energy levels. When making your own bone broth, make sure to use only the best chicken or beef from organically raised, pastured or grass fed animals. Bone Broth Recipe.
2. Collagen Supplements
While collagen sources in food exist, it can be hard to consume the parts of the animals where the collagen is concentrated.
Collagen Powder (the hydrolysed form of gelatin) is typically easier to digest and is often suggested for people with digestive problems. One advantage to this particular form of collagen is that it easily mixes into most hot and cold drinks and is tasteless, making it easy to add to foods and drinks for consumption.
Smart and convenient choices are the use of collagen supplements like Bovine collagen, chicken collagen or fish collagen.
Fish collagen: This is the one I use. Collagen derived from fish has been found to be easily absorbed and provide mostly type 1 collagen, with the amino acids glycine, proline and hydroxyproline. Because type 1 can be found throughout the entire body, consuming more fish collagen has been associated with benefits for the joints, skin, vital organs, blood vessels, digestion and bones.
Bovine collagen is also known as bovine cartilage or beef collagen. Gelatin is a form of hydrolysed beef collagen, which means it is essentially a part of broken-down collagen. Bovine collagen is a naturally occurring protein found in the cartilage, bones and hides of cows. This type of collagen is very similar to what we have in our bodies and provides a healthy dose of types 1 and 3 collagen.
It is a rich supply of glycine and proline, and therefore useful for creatine production, building muscle and also helping the body make its own collagen.
Chicken collagen: The type of collagen most abundant in chicken is type 2, which is best for building cartilage. This makes it beneficial for joint health.
This source also provides chondroitin sulphate and glucosamine sulphate — substances, both of which have a beneficial effects on the joints and have anti-aging effects. Most supplements containing collagen usually use chicken collagen and provide type 2.
3. Vegan And Non-Vegan Friendly Ways To Boost Collagen
Red light therapy / low-light wavelengths. Studies say red light therapy, increases collagen growth and hereby help reducing wrinkles and improving skin elasticity.
Retinol also known as vitamin A1 is an antioxidant used to increase the lifespan of collagen and block enzymes that destroy it.
Vitamin A is available in two forms, retinol and beta-carotene. Retinol is found in animal products and beta-carotene in fruits and vegetables. Retinol is the most readily absorbed form of vitamin A. While beta-carotene is not as readily absorbed, it can be converted into retinol within the body.
Foods rich in the beta-carotene form of vitamin A:
Broccoli
Carrots
Grapefruit
Guava
Kale
Mango
Melon
Papaya
Peppers
Pumpkin
Spinach
Squash
Tomato
Ginseng, with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, can increase collagen in the bloodstream and may have anti-aging benefits. (6)
Aloe vera, taken orally, can possible doubled hyaluronic acid and collagen production. (7)
Hyaluronic acid is a type of carbohydrate naturally found in the body. It lubricates and hydrates the eyes and the joints, has been used as a treatment for osteoarthritis and it is an important compound for collagen in the skin.
Hyaluronic acid can be consumed either through a supplement or a diet containing foods that are natural sources of this nutrient.
Hyaluronic acid is found in:
Beans
Soy products
Root vegetables
Leafy greens
And homemade broths made from organic animal bones, skin and connective tissues are even better sources of hyaluronic acid.
Have your collagen with some vitamin-C. Hydroxyproline is an important component of collagen, and lower levels have been associated with joint degradation and therefore symptoms/signs of aging. Hydroxyproline is needed for collagen stability and is created by modifying normal proline amino acids after the collagen chain is built. This reaction also requires vitamin C (to assist in the addition of oxygen), which is why vitamin C deficiency can cause abnormalities in collagen levels.
And note that essential vitamin C was shown in one study to be skin protective and create more collagen in the body.
Foods high in vitamin C:
Bell Peppers
Berries
Broccoli
Citrus Fruits
Dark Green Leafy Vegetables
Guavas
Kiwifruit
Papaya
Peas
Tomatoes
Antioxidants protect against damaging free radicals, and enhance the effectiveness of existing collagen.
Foods high in Antioxidants:
Apples
Artichokes
Beans
Blackberries
Cilantro
Cranberries
Dark chocolate
Elderberries
Pecans
Plums
Prune
Raspberries
MSM (methylsulfonylmethane). Though the name sounds intimidating MSM is basically sulphur and it is in our bodies, as well as in some plants. It is composed of sulphur, oxygen and methyl. MSM has the ability to enhance collagen and it's necessary for collagen production.
MORE: 7 Amazing Beauty and Health Benefits of MSM
How To Choose Collagen Supplement
There are several good sources of high-quality bone broth and collagen powders. When sourcing, it is important to make sure that it is obtained from grass-fed and pastured humanely raised sources or from fresh Non-GMO verified wild-caught fish and from a reputable company. I prefer Vital Proteins. or Great Lakes.
I prefer this marine collagen.
You can buy organic chicken bone broth collagen.
Collagen Peptides sourced from grass-fed, pasture-raised bovine hides.
Collagen Supplements For Vegans And Vegetarians:
This Biotin and vitamin C rich supplement help boost the body’s natural production of collagen.
Disclaimer:
All information in this blog is strictly for informational purposes only and should not be taken as medical advice. The statements made in this blog have not been evaluated by The Danish Health Authority. The products linked to in this blog and any information published in this blog are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. The information provided by this blog is not a substitute for a face to-face consultation with your physician, and should not be construed as medical advice. The entire contents of this blog are based upon the opinions of Hanne Robinson. By reading and using this blog, you agree to only use this publication for personal informational use and not as a substitute for medical or other professional advice.